Bilberry Leaf
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
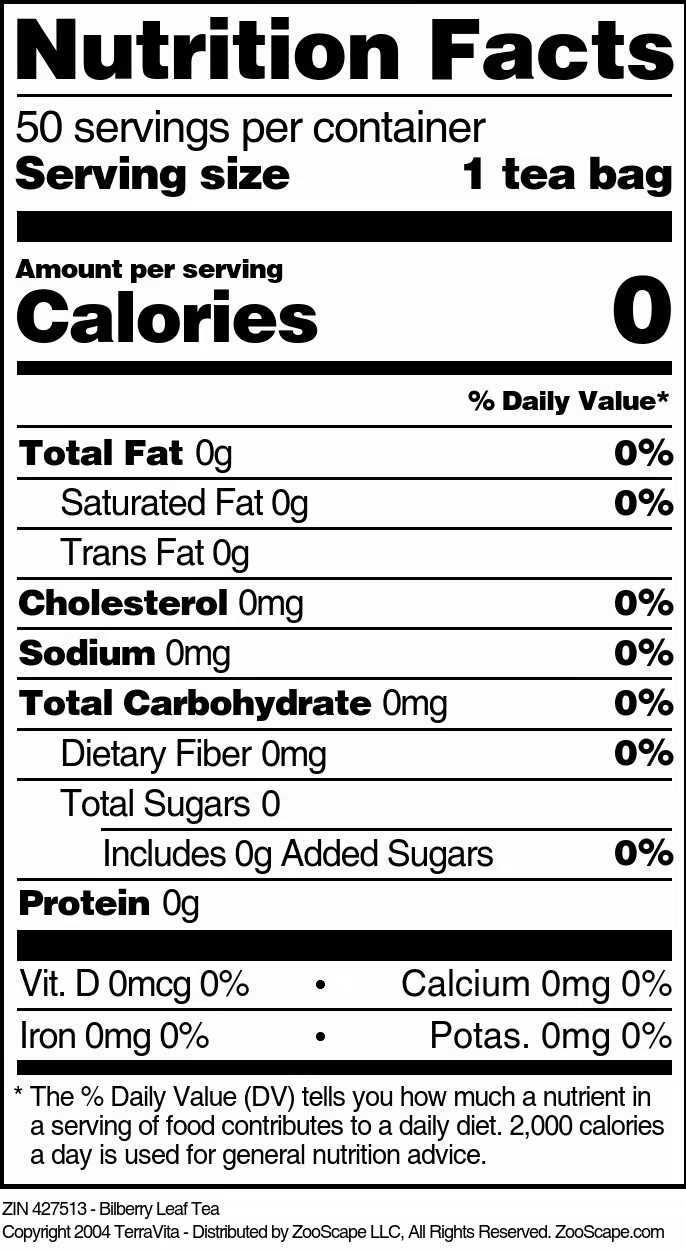
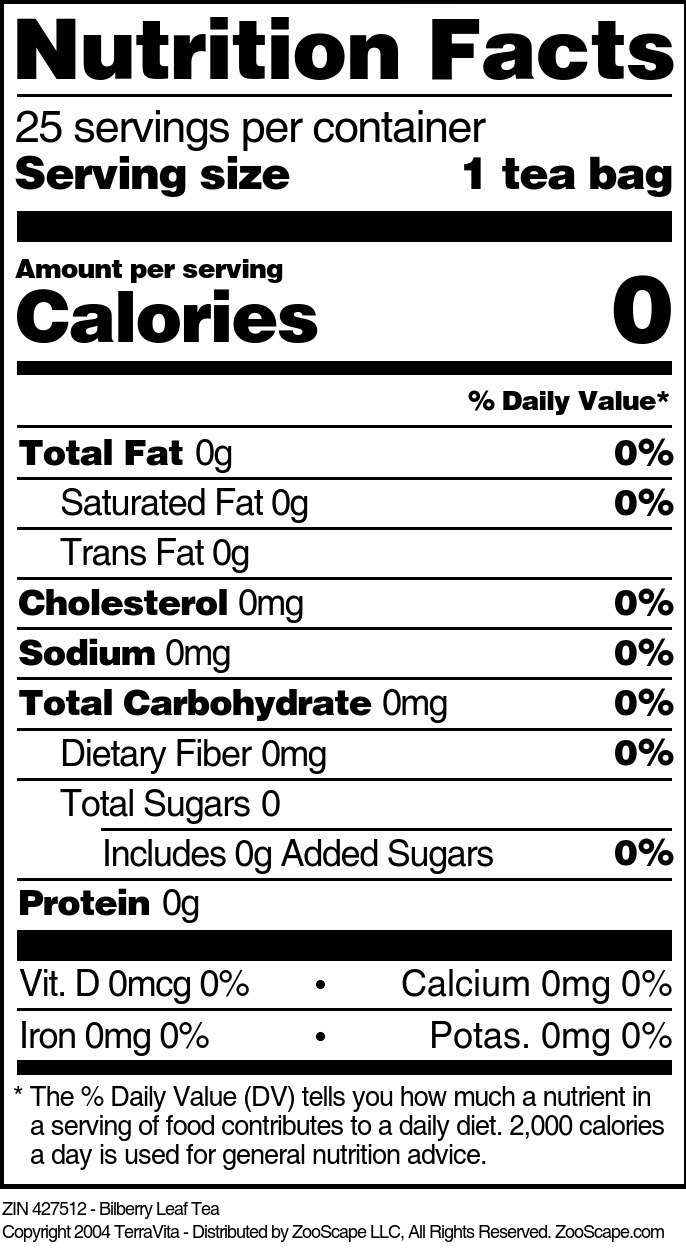
| Bilberry Leaf Tea | 25 tea bags | 427512 | $17.37 | |||
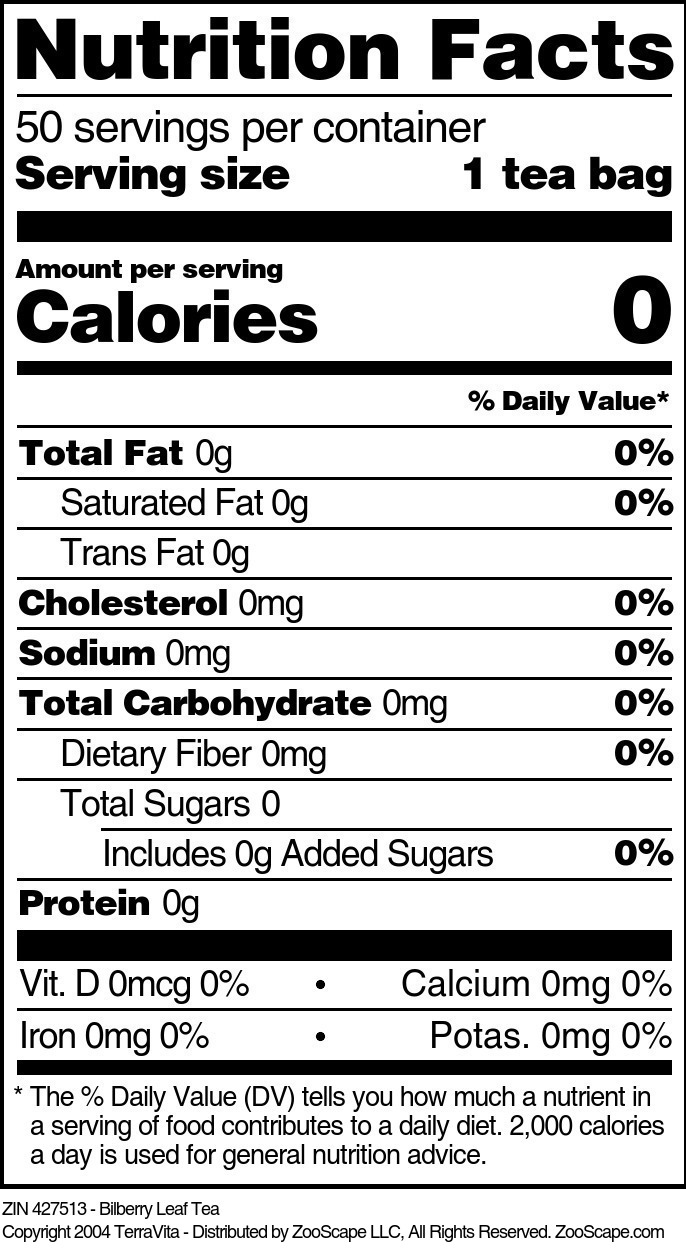
| 50 tea bags | 427513 | $32.00 | ||||
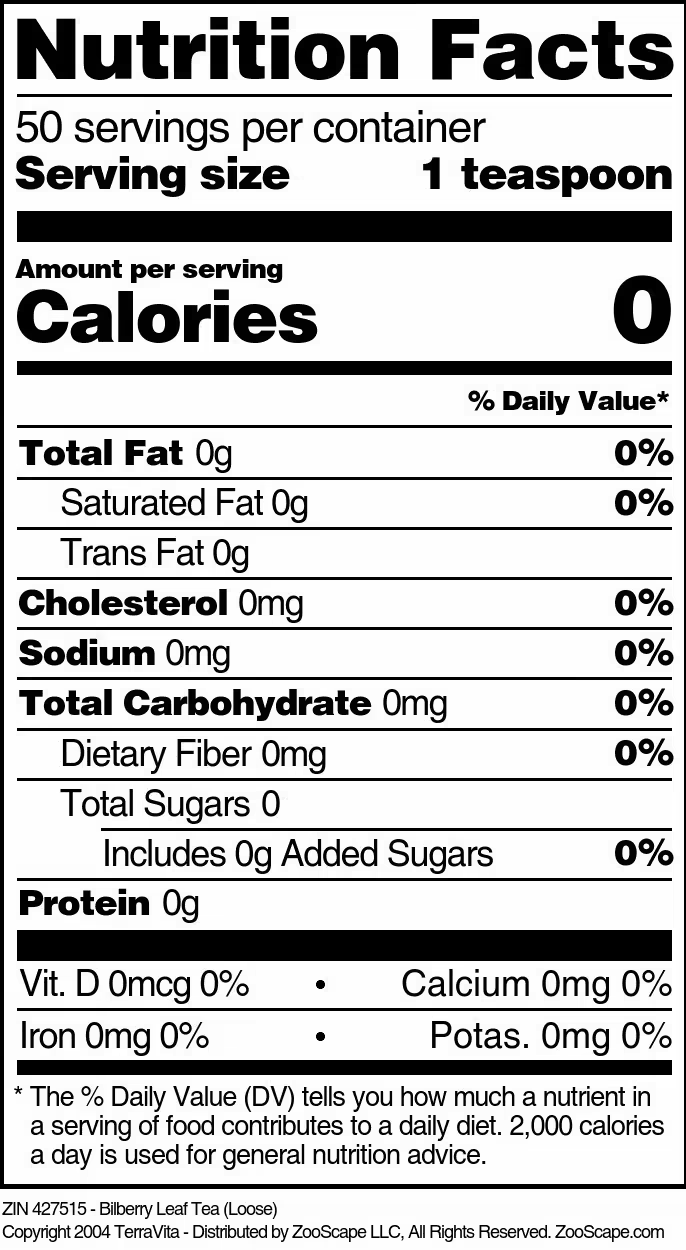
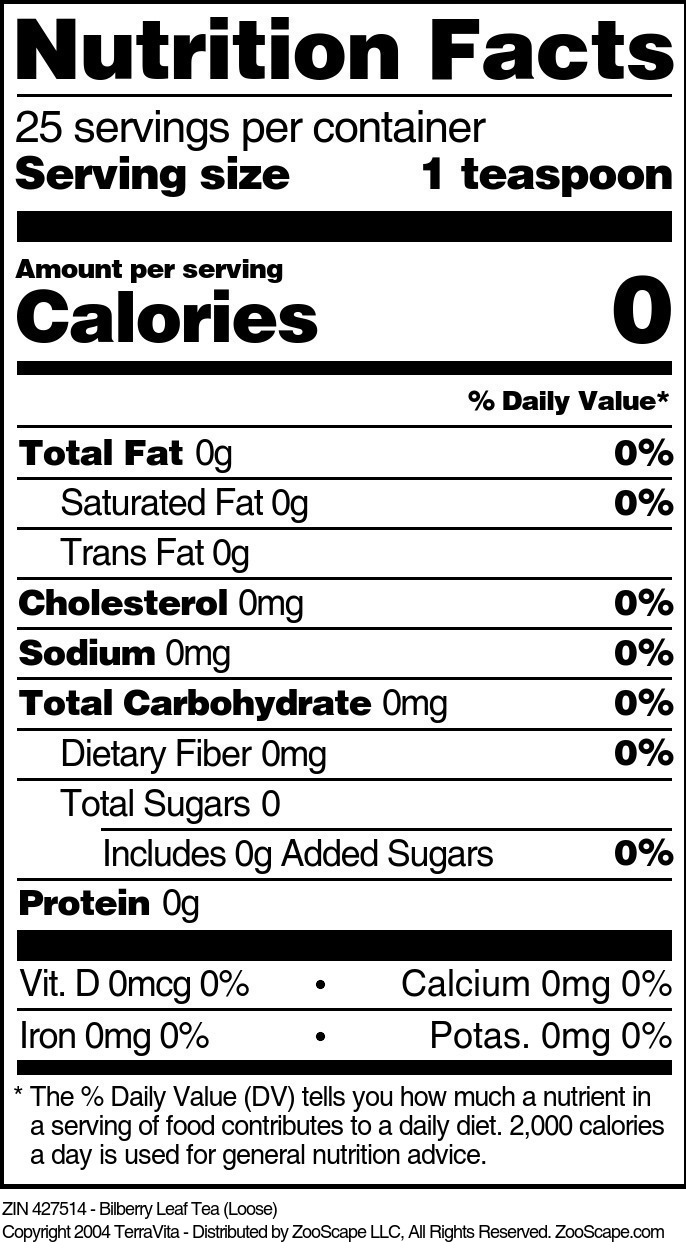
| Bilberry Leaf Tea (Loose) | 4 oz | 427514 | $17.94 | |||
| 8 oz | 427515 | $28.85 | ||||
| Bilberry Leaf - Glycerite Liquid Extract (1:5) | 1 fl oz - No Flavor | 428072 | $14.84 | |||
| 1 fl oz - Strawberry | 428073 | $18.89 | ||||
| Bilberry Leaf - Salve Ointment | 2 oz | 428074 | $34.39 | |||
| Bilberry Leaf - Cream | 2 oz | 428075 | $27.68 | |||
| Bilberry Leaf - Glycerite Liquid Extract (1:5) | 1 fl oz - Chocolate | 428217 | $18.89 | |||
| 1 fl oz - Vanilla | 428241 | $18.89 | ||||
| 1 fl oz - Mint | 428299 | $18.89 | ||||
| Bilberry Leaf - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 510961 | $24.16 | |||
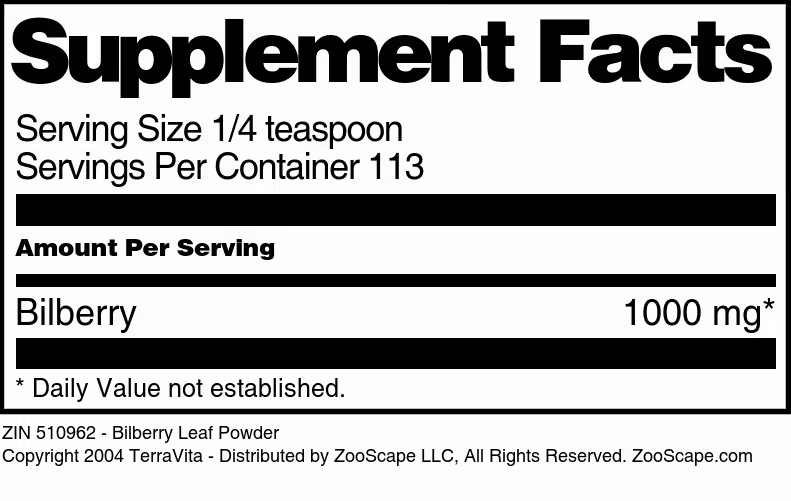
| Bilberry Leaf Powder | 4 oz | 510962 | $22.35 | |||
| 1 oz | 510963 | $11.24 |
• Once popular berry in pies and fillings exhibits powerful vision supporting properties!
• Clinical trials establish benefits for those with eye health concerns.
• Exhibits disinfectant, and anti-spasmodic properties for additional potential health benefits.
• Approved by German health authorities!
• All the proven health benefits of bilberry in a delicious drink!
• Purists insist on loose tea for a superior cup of tea!
• No fillers or extenders!
• No artificial colors or flavors!
• 100% natural bilberry glycerite!
• All the benefits of bilberry with the delicious flavor of strawberries!
• A taste kids will love!
• Maintaining healthy eyes never tasted so good!
• Take care of your eyes and give your taste buds a break, too!
• Delicious vanilla flavor with all the natural herbal goodness of bilberry!
• 100% additive-free formulation!
• Vision support with a minty fresh appeal!
• So refreshing, you'll never miss a dose!
• Gelatin capsule offers convenience, simplicity, and excellent absorption!
• For accuracy of dosage and consistency on a day-to-day basis when optimizing your health!
• Versatile powdered form means lots of dietary options!
• Pure powder with no fillers or extenders adds up to pure value!
• Try delicious bilberry powders on breakfast cereals!
• Add this blueberry flavored supplement to smoothies for a tasty way to take care of your eyes!
Plant Facts and Growing Tips
Plant: A shrubby, deciduous perennial with angular, branched stems that grow from a creeping woodstock. The leaves are dark green and shiny, about 1/2 to 1 inch long. Reddish pink or red and white flowers are produced in May and June. The fruit is a blue-black, reddish, five-seeded berry. Although sometimes called a huckleberry, it more closely resembles a cranberry, and is a relative of bearberry.
Height: 1 to 2 feet.
Soil: Sandy, peaty, acidic in northern United States; woods and forest meadows in Europe. Bilberry doesn't like limy soils.
Exposure: Sun.
Propagation: Division of rhizomes or clumps, layering, cuttings.
Parts Used for Tea: Leaves and berries. Gather leaves when the plant is fully developed but before the berries are ripe. Collect berries and dry them. When ripened, they have the highest vitamin and mineral content.
Taste: Sour, astringent, cold, dry.
How to Brew
By Infusion: Steep 2 to 3 teaspoons leaves in 1 cup water. Drink one cup per day.
By Decoction: Steep 1 teaspoon dried berries with 1 cup water. Drink one or two cups per day, cold. Lemon rinds blend nicely with the decoction and add a tangy flavor.
Bilberry Fruit Tea
In a large punch bowl, add your choice of diced fruits and juices, sprigs of mint, apple cider, and lemon juice. Then add cold bilberry tea for flavor and color.
Potential Health Benefits
Commission E endorses the dried, ripe fruit and preparations made from it for use against acute diarrhea and to soothe sore throats. Broad claims by some writers that bilberry reduces macular degeneration in the eye, help promotes night vision, and serves as a supersaver of eyesight weren't addressed by Commission E.
Scientific Evidence
Bilberry preparations contain tannins, flavonoid glycosides, and anthocyanosides. Flavonoids and anthocyanosides are credited with producing the salutary health benefits of red wine and grape juice. In laboratory tests, flavonoids fight the oxidization of low-density cholesterol, which suggests they might be useful for avoiding coronary heart health issues. Without cit ing specifics, health writer James A. Duke, Ph.D., alludes to research in the 1990s that he says "has demonstrated bilberry's efficacy in supporting circulatory complications due to blood sugar level issues or hypertension, bruising, capillary fragility, varicose veins, hemorrhoids, and Raynaud's phenomenon." Commission E's report, published in 1994, doesn't address these much broader uses of bilberry fruit. Bilberry leaf was listed as unapproved by the commission, which favors the fruit.)
How to Use the Herb
For internal use, take a daily dose of 20-60 grams, or 1 to 2 ounces of the dried berry. Bilberry tea can be made by putting 1-2 teaspoonfuls of crushed berries in cold water, soaking for 10 minutes, and straining. Supplements set at 80-100 milligrams, taken 3 times per day, are recommended by a variety of health writers. James A. Duke recommends capsules that are standardized to 25 percent anthocyanosides.
TerraVita is an exclusive line of premium-quality, natural source products that use only the finest, purest and most potent ingredients found around the world. TerraVita is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, potency, stability and freshness. All of our products are prepared with the highest elements of quality control, from raw materials through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the bottles or bags are sealed for freshness and shipped out to you. Our highest possible standards are certified by independent laboratories and backed by our personal guarantee.
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
TerraVita is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
Bianca Rosa is an exclusive line of premium-quality natural products sourced from only the finest and purest ingredients from around the world. Bianca Rosa is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, stability and freshness. All Bianca Rosa products are prepared with the highest level of quality control, from the raw materials used through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the finished product is sealed for freshness and shipped to you. Our highest possible standards backed by our personal guarantee.
Bianca Rosa makes all products as affordable as possible and we are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you. Bianca Rosa has been a trusted household name for many families throughout the world since the 1990s. Bianca Rosa is packed in tamper-proof, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of all Bianca Rosa products, including creams, salves and oils in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
The TerraVita Premium Collection uses only the finest, purest and most potent plant extracts from around the world.
The TerraVita Premium Collection is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, potency, stability and freshness. Our highest possible standards are certified by independent laboratories and backed by our personal guarantee.
The TerraVita Premium Collection is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.
Bilberry Leaf 4:1 Extract
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
| Extra Strength Bilberry Leaf 4:1 Extract - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 511245 | $25.21 | |||
| Extra Strength Bilberry Leaf 4:1 Extract Powder | 4 oz | 511246 | $24.80 | |||
| 1 oz | 511247 | $11.41 | ||||
| Extra Strength Bilberry Leaf 4:1 Extract Cream | 2 oz | 514095 | $25.90 | |||
| Extra Strength Bilberry Leaf 4:1 Extract - Salve Ointment | 2 oz | 514096 | $30.70 |
• Ideal for complaints that may require added bilberry strength and potency !
• Powerful extract with highly concentrated active bilberry compounds!
• Exceptional value with lots of options as a meal or beverage additive!
• Effective as a supportive for healthy vision, macular degeneration, circulation problems and much more.
Bilberry
Vaccinium myrtillus L.
Family: Ericaceae.
Other Names: Blueberry; airelle myrtille (French); Heidelbeere, Blaubeere (Germany); mirtillo (Italian); arandano commun (Spanish).
Description: Bilberry is a common shrublet (up to 0.8 m) with small toothed leaves, white, bell-shaped flowers and purplish blue berries (8 mm diameter).
Origin: Cold temperate parts of the northern hemisphere (common in Europe, but also in Asia and North America). Berries and leaves are wild-harvested.
Parts Used: Dried, ripe berries (Myrtilli fructus) and to a lesser extent the leaves (Myrtilli folium).
Therapeutic Category: Anti-diarrhoeal.
Preparation and Dosage: A daily dose of 20 - 60 g of dried berries is recommended. The leaves are no longer recommended because prolonged use seemed to have toxic side effects.
Active Ingredients: The main active ingredients are mostly catechol tannins (up to 12%) and proanthocyanidins. Also present are anthocyanins, flavonoids, iridoids glycosides (asperuloside, monotropein) and phenolic acids. Similar compounds are present in the leaves. Aerial parts contain a simple bicyclic quinolizidine alkaloid, epimyrtine. Arbutin and other hydroquinones are more or less absent.
Health Effects: The product reduces the levels of blood lipids and glucose; it has anti-exudative and anti-ulcus activity, can help improve the permeability of capillaries and wound-mending and inhibits platelet aggregation. These properties can be partly explained by the secondary metabolites present; clinical studies are needed to substantiate the claims.
Notes: Bog bilberry (V. uliginosum) has similar phytochemicals and can be used like bilberry. Cowberry (V. vitisidaea) is rich in tannins, proanthocyanidins and arbutin. Leaves are a traditional antiseptic diuretic used to help support infections of the urinary tract.
Status: Traditional health; Pharm.; Comm. E+ (fruit only).
Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) is a short, shrubby perennial plant that inhabits the woods and forest meadows of Europe, western Asia, and the Rocky Mountains of North America. As with many other plants that belong to the same plant family (Vaccinium), bilberry bears edible fruits similar to those found on the blueberry bush. Cranberries and huckleberry belong to this plant family
The bilberry's blue-black berry, which is creamy white inside, has been valued as a food since prehistoric times. Commonly referred to as "European Blueberry," it is famed as a filling for pies, and for use in cobblers, jams, and other recipes.
In addition, for at least one thousand years, European herbalists have also recommended the plant's fruits and leaves for health purposes, addressing a variety of complaints with a strong, boiled tea made from the plant. Urinary tract health concerns, kidney stones, and diarrhea are just a few of the ailments for which bilberry can be been used as a supportive.
Bilberry's modern reputation as a rejuvenating plant was sparked during World War II, when British Royal Air Force (RAF) pilots noticed that their night vision was sharper than usual whenever they ate bilberry preserves before starting out on their evening bombing raids. Subsequent research revealed that bilberries are powerful antioxidants, capable of protecting cells in the eye and other parts of the body against damage from unstable oxygen molecules called free radicals.
Today, bilberry ranks among the most popular of supplements for maintaining healthy vision and for the potential to help support symptoms of various vision disorders, including poor night vision, vision, and macular degeneration.
Health Benefits:
Researchers intrigued by the improved night vision of the bilberry-eating RAF pilots eventually identified compounds in the berry called anthocyanosides. These substances appear to fortify blood vessel walls, improving blood flow to the tiny blood vessels that keep eyes healthy, and to larger blood vessels that help maintain good circulation throughout the body. Anthocyanosides also appear to strengthen collagen, the protein that provides support to mend connective tissue.
The other important healing substance in bilberry fruits - astringent compounds called tannins - help support such ailments as diarrhea, sore throat, and inflammations in the mouth. Germany health authorities approve of bilberry fruit for mild cases of diarrhea and mouth and throat inflammation. A cooled tea made from the dried berries can be either drunk or gargled for these purposes.
The TerraVita Premium Collection is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, potency, stability and freshness. Our highest possible standards are certified by independent laboratories and backed by our personal guarantee.
The TerraVita Premium Collection is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
Bianca Rosa is an exclusive line of premium-quality natural products sourced from only the finest and purest ingredients from around the world. Bianca Rosa is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, stability and freshness. All Bianca Rosa products are prepared with the highest level of quality control, from the raw materials used through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the finished product is sealed for freshness and shipped to you. Our highest possible standards backed by our personal guarantee.
Bianca Rosa makes all products as affordable as possible and we are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you. Bianca Rosa has been a trusted household name for many families throughout the world since the 1990s. Bianca Rosa is packed in tamper-proof, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of all Bianca Rosa products, including creams, salves and oils in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.
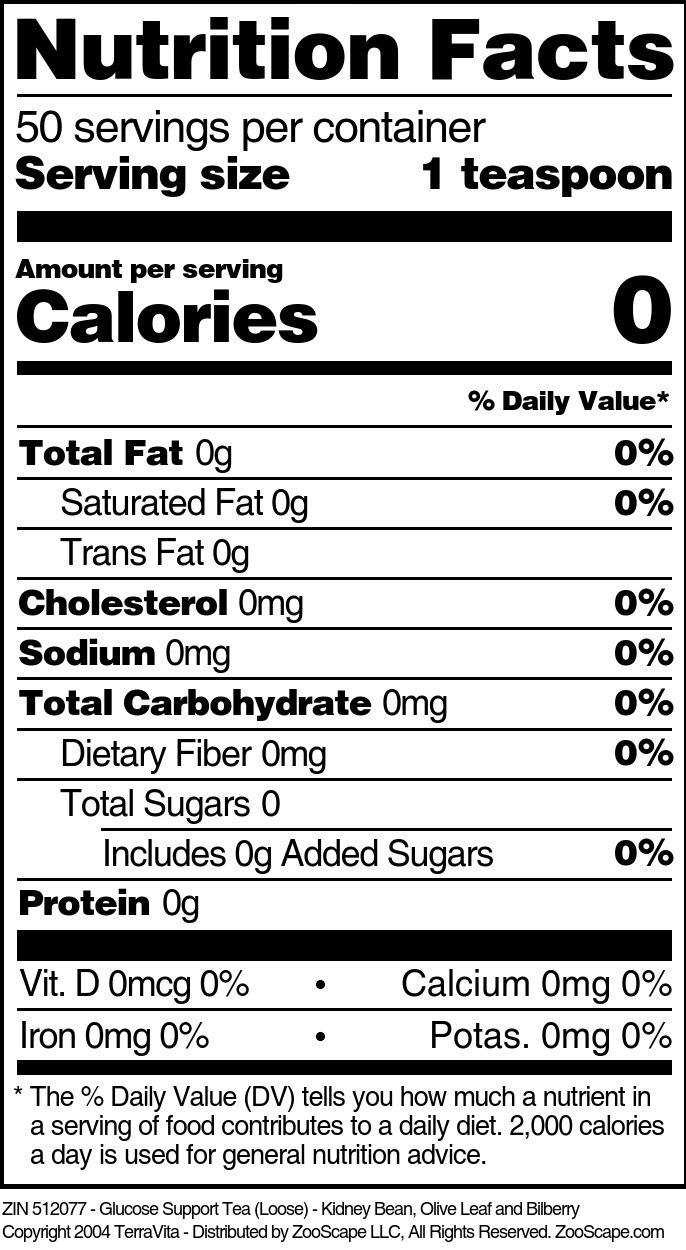
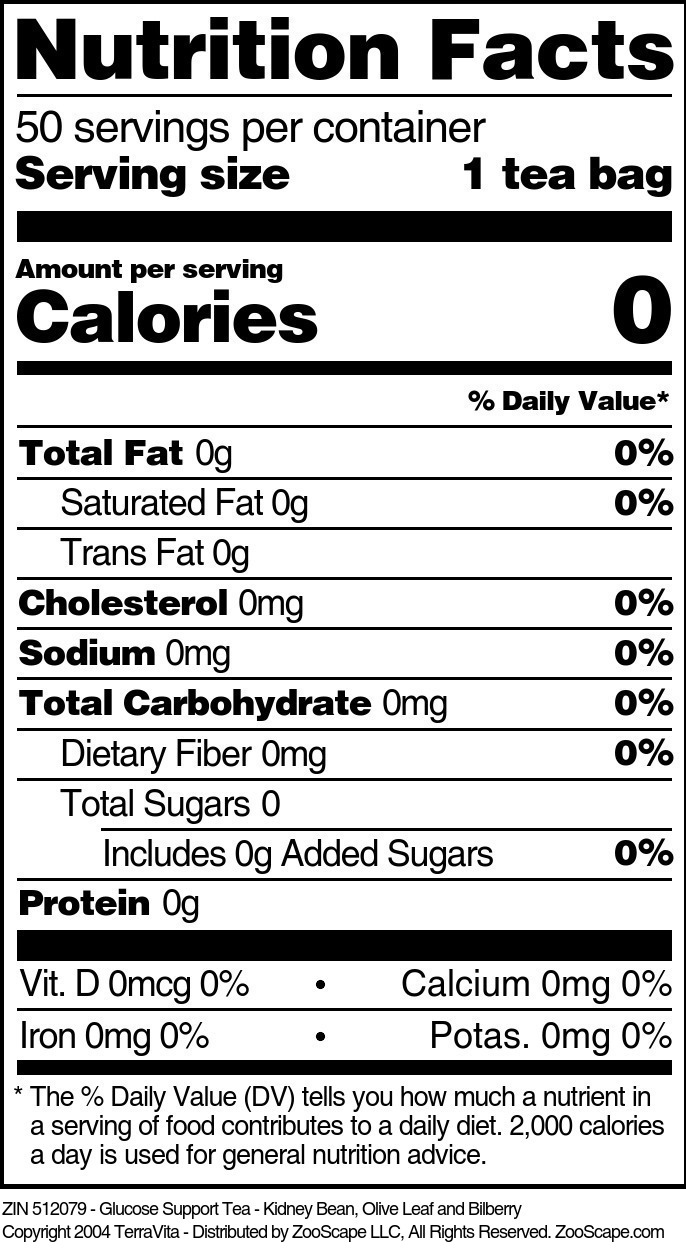
Glucose Support
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
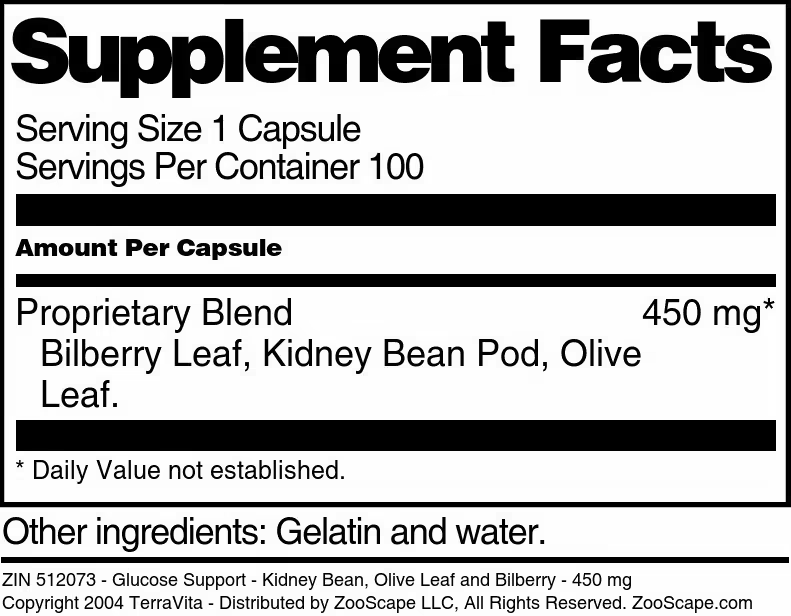
| Glucose Support - Kidney Bean, Olive Leaf and Bilberry - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 512073 | $22.47 | |||
| Glucose Support Powder - Kidney Bean, Olive Leaf and Bilberry | 4 oz | 512074 | $20.25 | |||
| 1 oz | 512075 | $10.14 | ||||
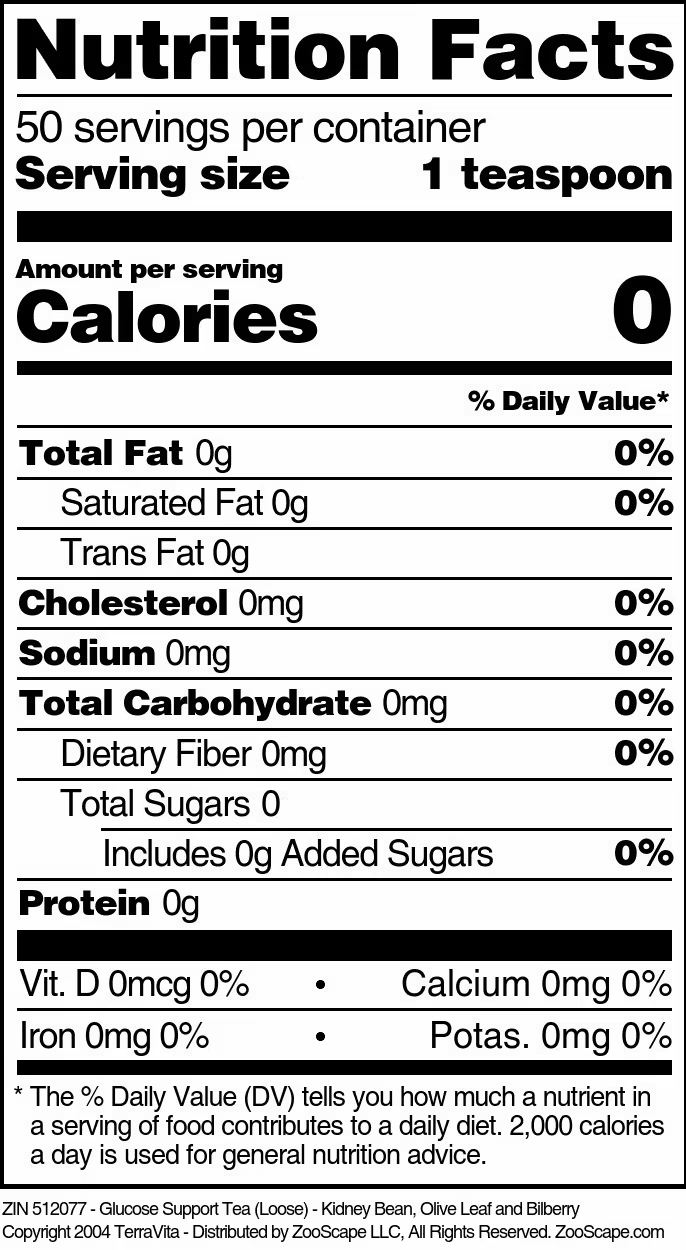
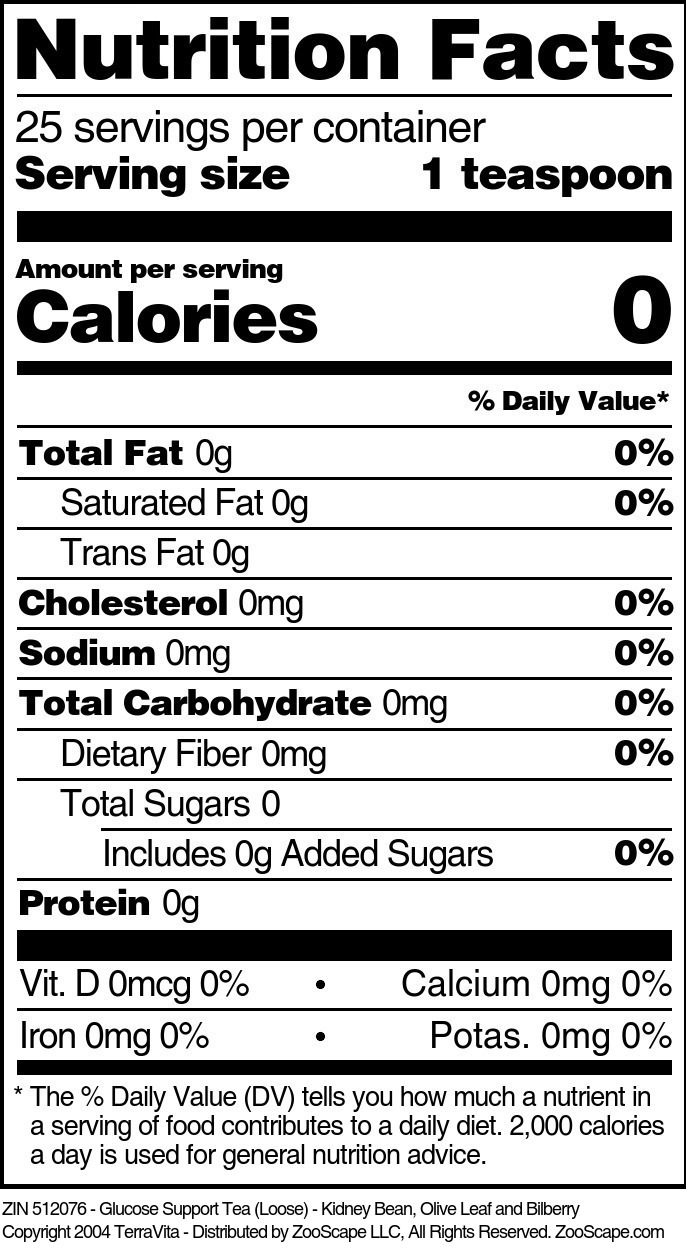
| Glucose Support Tea (Loose) - Kidney Bean, Olive Leaf and Bilberry | 4 oz | 512076 | $16.41 | |||
| 8 oz | 512077 | $24.50 | ||||
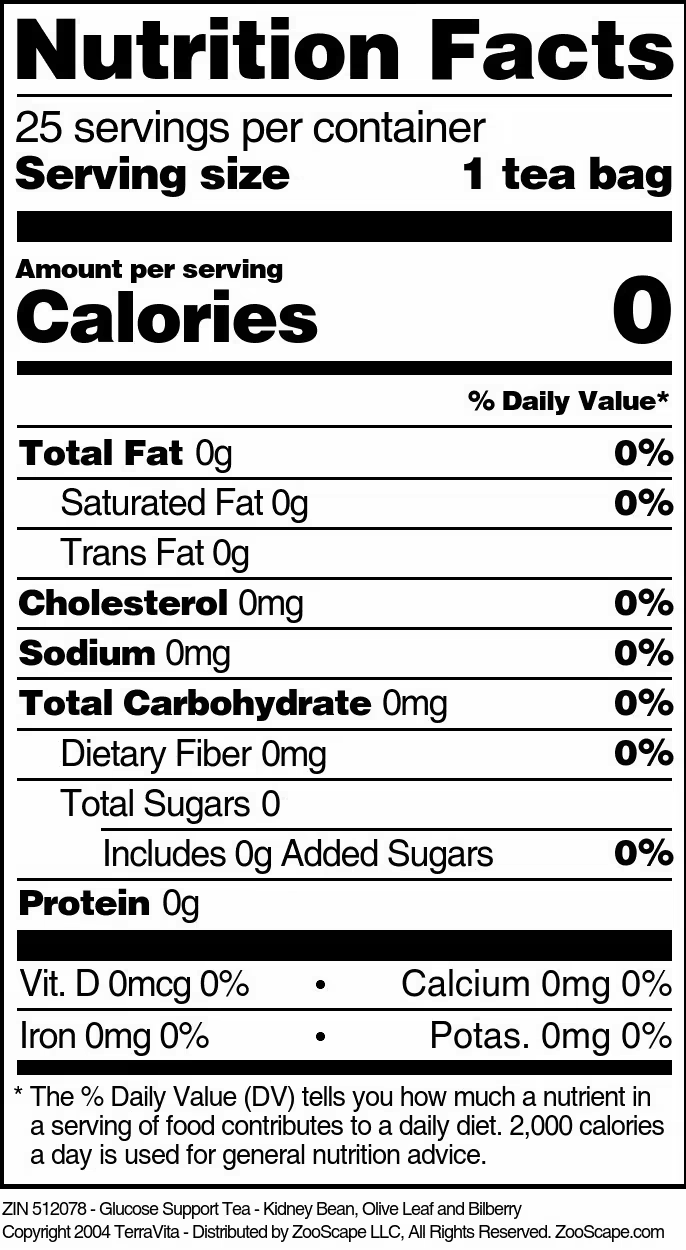
| Glucose Support Tea - Kidney Bean, Olive Leaf and Bilberry | 25 tea bags | 512078 | $16.48 | |||
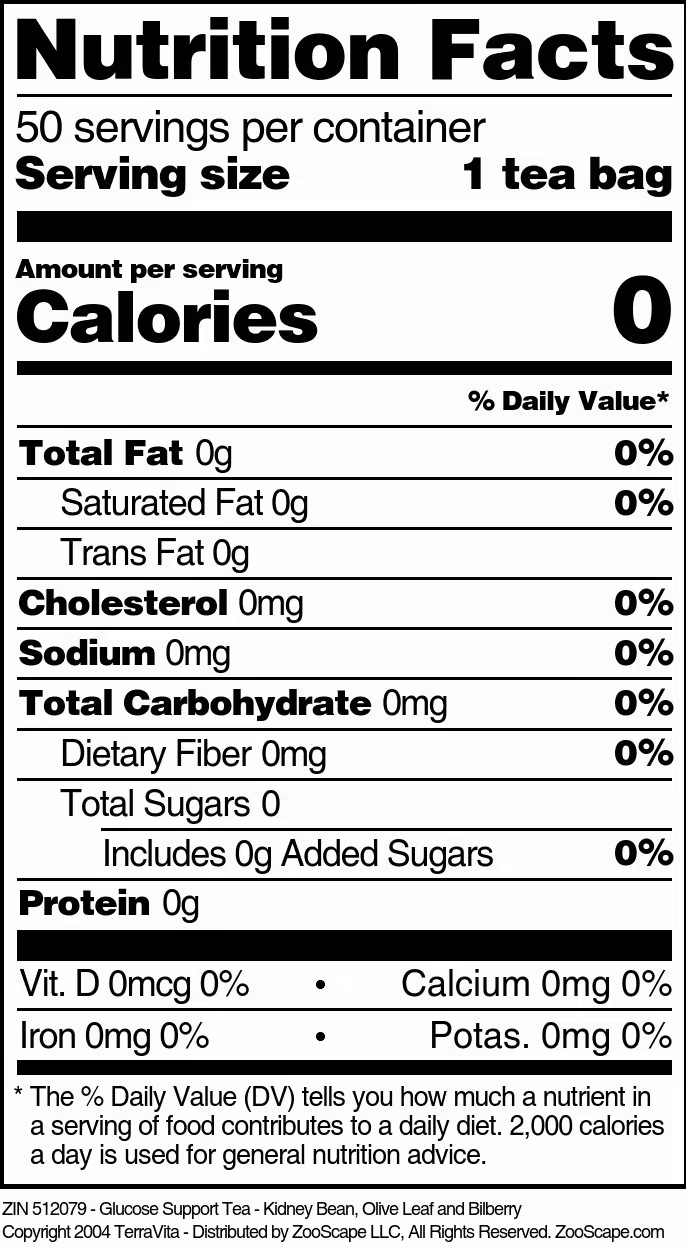
| 50 tea bags | 512079 | $25.42 | ||||
| Glucose Support Glycerite Liquid Extract (1:5) | 1 oz - No Flavor | 523561 | $20.16 | |||
| 1 oz - Strawberry | 523562 | $22.29 | ||||
| 1 oz - Vanilla | 523563 | $22.29 | ||||
| 1 oz - Chocolate | 523564 | $22.29 | ||||
| 1 oz - Mint | 523565 | $22.29 |
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
TerraVita is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
TerraVita is an exclusive line of premium-quality, natural source products that use only the finest, purest and most potent ingredients found around the world. TerraVita is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, potency, stability and freshness. All of our products are prepared with the highest elements of quality control, from raw materials through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the bottles or bags are sealed for freshness and shipped out to you. Our highest possible standards are certified by independent laboratories and backed by our personal guarantee.
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.
Diabetes
(Type I and Type II) Support
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
| Blood Sugar Support - Gymnema, Fenugreek, Bilberry and More - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 517141 | $23.40 | |||
| Blood Sugar Support Powder - Gymnema, Fenugreek, Bilberry and More | 4 oz | 517142 | $21.80 | |||
| 1 oz | 517143 | $10.58 |
Modern research indicates that fenugreek seed not only stimulates insulin secretion and supports healthy blood sugar levels, but it can lower bad cholesterol levels (LDL) while elevating good cholesterol (HDL).
Bilberry is included in this formula as a blood vessel protector, since damage to the eyes, kidneys, and extremities may result.
Grape seed extract, rich in flavonoids, provides additional circulatory support similar to that of bilberry.
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
TerraVita is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.
Bilberry 10:1 Extract
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
| Bilberry 10:1 - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 519177 | $128.42 | |||
| Bilberry 10:1 Powder | 1 oz | 519178 | $56.42 | |||
| 4 oz | 519179 | $119.33 | ||||
| Bilberry 10:1 Cream | 2 oz | 519180 | $177.19 | |||
| Bilberry 10:1 Salve | 2 oz | 519181 | $194.38 |
Latin Botanical Name: Vaccinium Myrtillus
Plant Parts Used: Fruit
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
TerraVita is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
Bianca Rosa is an exclusive line of premium-quality natural products sourced from only the finest and purest ingredients from around the world. Bianca Rosa is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, stability and freshness. All Bianca Rosa products are prepared with the highest level of quality control, from the raw materials used through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the finished product is sealed for freshness and shipped to you. Our highest possible standards backed by our personal guarantee.
Bianca Rosa makes all products as affordable as possible and we are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you. Bianca Rosa has been a trusted household name for many families throughout the world since the 1990s. Bianca Rosa is packed in tamper-proof, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of all Bianca Rosa products, including creams, salves and oils in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.
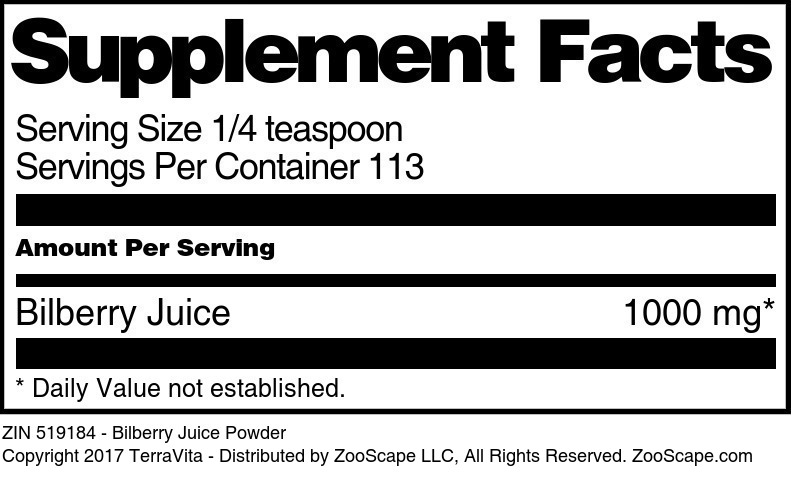
Bilberry Juice
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
| Bilberry Juice - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 519182 | $55.18 | |||
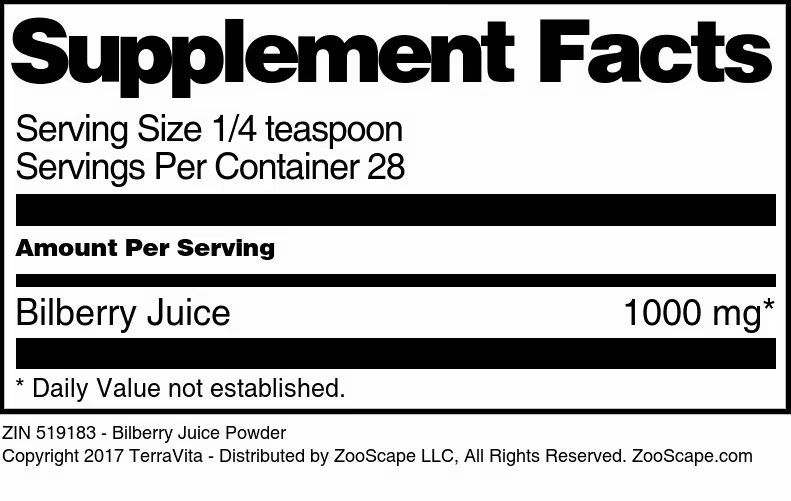
| Bilberry Juice Powder | 1 oz | 519183 | $24.24 | |||
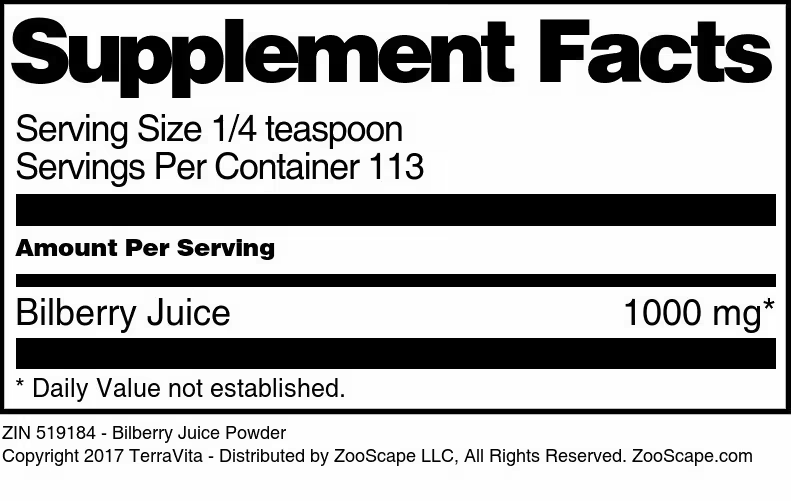
| 4 oz | 519184 | $51.27 | ||||
| Bilberry Juice Cream | 2 oz | 519185 | $76.12 | |||
| Bilberry Juice Salve | 2 oz | 519186 | $83.51 |
Latin Botanical Name: Vaccinium Myrtillus
Plant Parts Used: Juice
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
TerraVita is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
Bianca Rosa is an exclusive line of premium-quality natural products sourced from only the finest and purest ingredients from around the world. Bianca Rosa is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, stability and freshness. All Bianca Rosa products are prepared with the highest level of quality control, from the raw materials used through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the finished product is sealed for freshness and shipped to you. Our highest possible standards backed by our personal guarantee.
Bianca Rosa makes all products as affordable as possible and we are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you. Bianca Rosa has been a trusted household name for many families throughout the world since the 1990s. Bianca Rosa is packed in tamper-proof, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of all Bianca Rosa products, including creams, salves and oils in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.
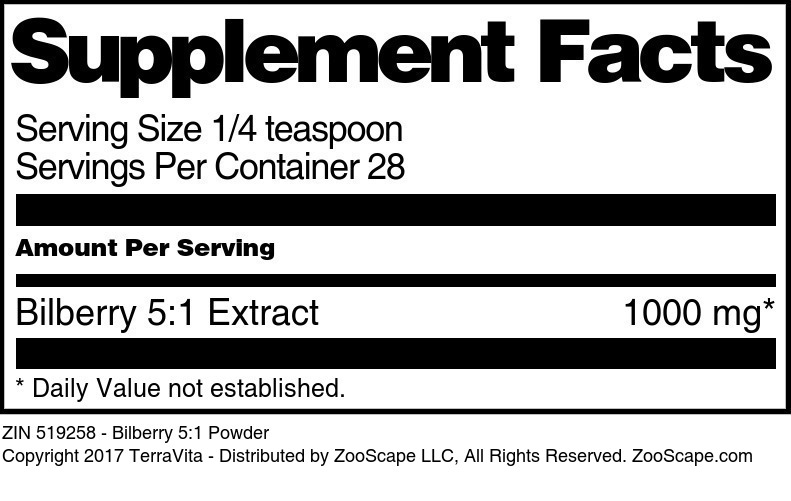
Bilberry 5:1 Extract
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
| Bilberry 5:1 - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 519257 | $57.90 | |||
| Bilberry 5:1 Powder | 1 oz | 519258 | $25.43 | |||
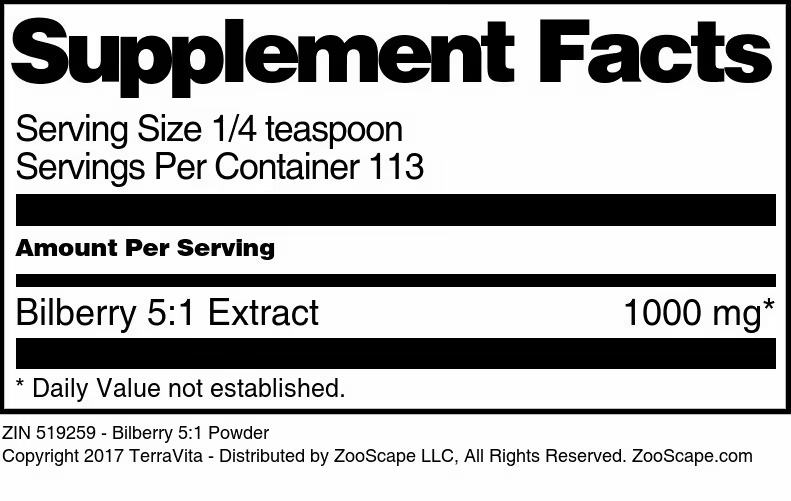
| 4 oz | 519259 | $53.81 | ||||
| Bilberry 5:1 Cream | 2 oz | 519260 | $79.89 | |||
| Bilberry 5:1 Salve | 2 oz | 519261 | $87.64 |
Latin Botanical Name: Vaccinium Myrtillus
Plant Parts Used: Fruit
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
TerraVita is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
Bianca Rosa is an exclusive line of premium-quality natural products sourced from only the finest and purest ingredients from around the world. Bianca Rosa is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, stability and freshness. All Bianca Rosa products are prepared with the highest level of quality control, from the raw materials used through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the finished product is sealed for freshness and shipped to you. Our highest possible standards backed by our personal guarantee.
Bianca Rosa makes all products as affordable as possible and we are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you. Bianca Rosa has been a trusted household name for many families throughout the world since the 1990s. Bianca Rosa is packed in tamper-proof, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of all Bianca Rosa products, including creams, salves and oils in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.
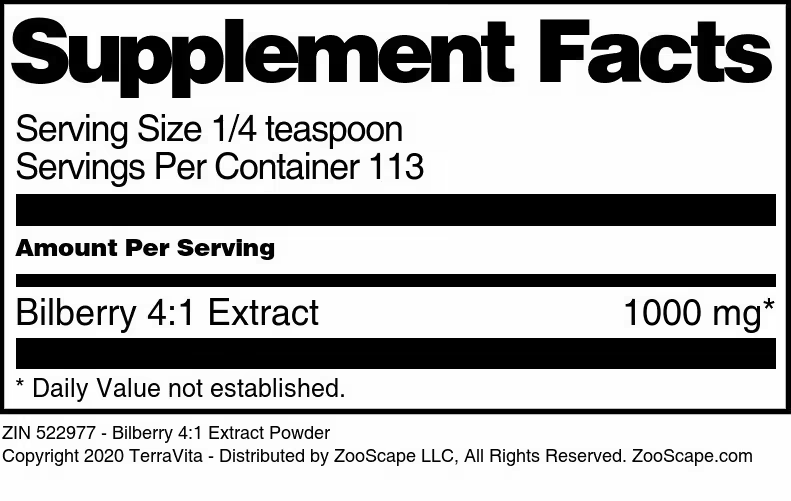
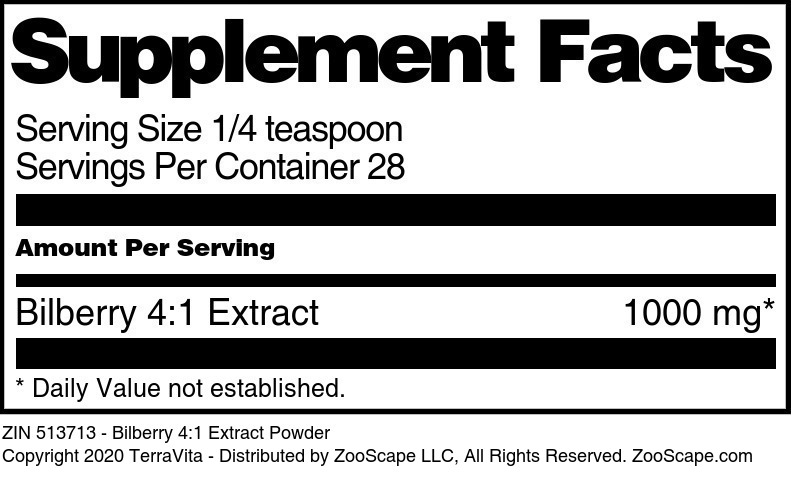
Bilberry 4:1 Extract
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
| Bilberry 4:1 Extract Cream | 2 oz | 523875 | $85.80 | |||
| Bilberry 4:1 Extract Salve | 2 oz | 523876 | $94.13 | |||
| Bilberry 4:1 Extract - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 513712 | $41.67 | |||
| Bilberry 4:1 Extract Powder | 1 oz | 513713 | $20.92 | |||
| 4 oz | 522977 | $49.95 |
Bianca Rosa makes all products as affordable as possible and we are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you. Bianca Rosa has been a trusted household name for many families throughout the world since the 1990s. Bianca Rosa is packed in tamper-proof, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of all Bianca Rosa products, including creams, salves and oils in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
TerraVita is an exclusive line of premium-quality, natural source products that use only the finest, purest and most potent ingredients found around the world. TerraVita is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, potency, stability and freshness. All of our products are prepared with the highest elements of quality control, from raw materials through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the bottles or bags are sealed for freshness and shipped out to you. Our highest possible standards are certified by independent laboratories and backed by our personal guarantee.
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
TerraVita is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.
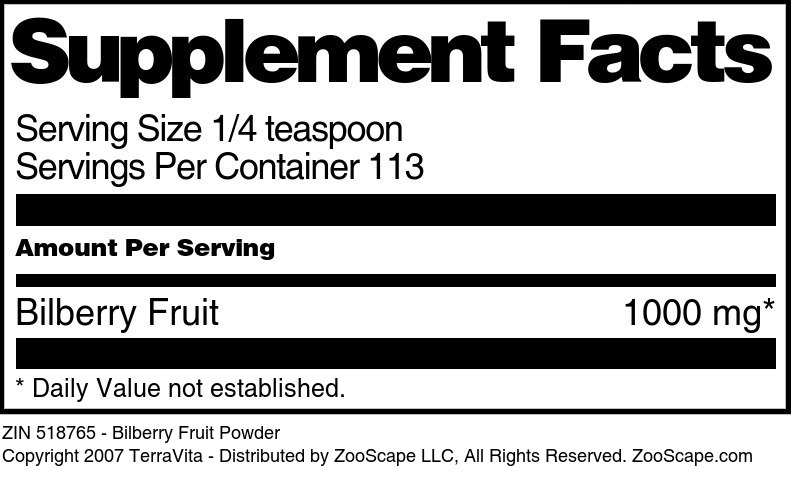
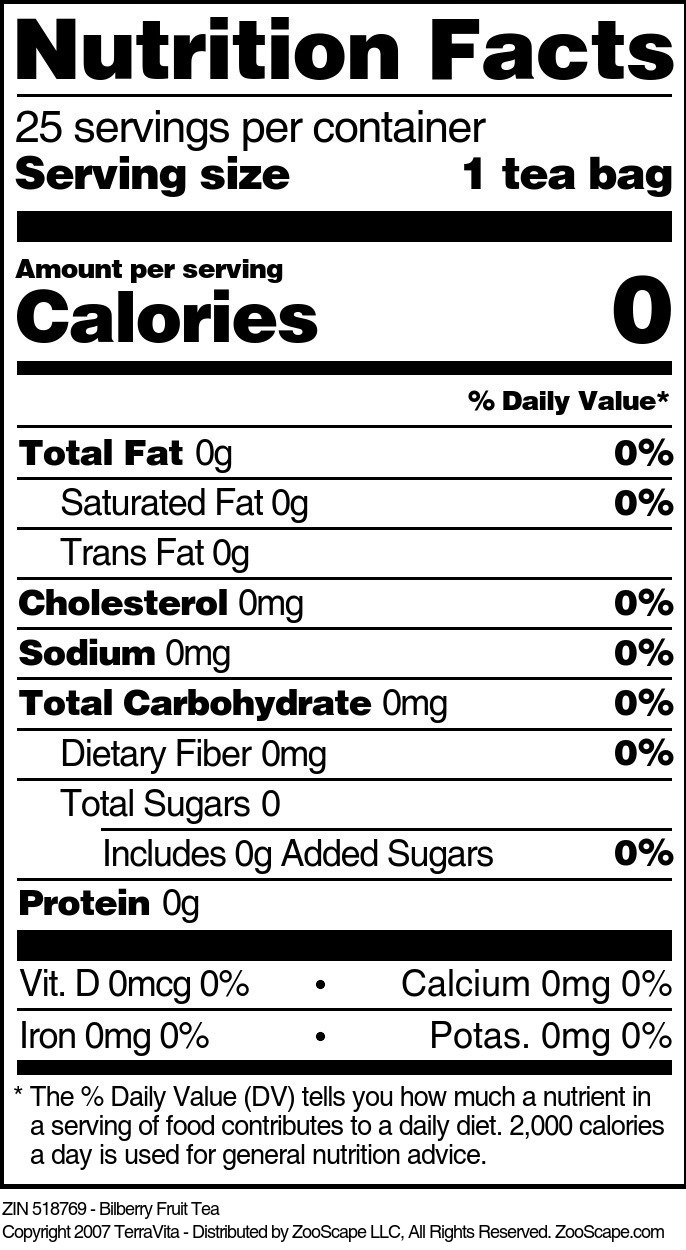
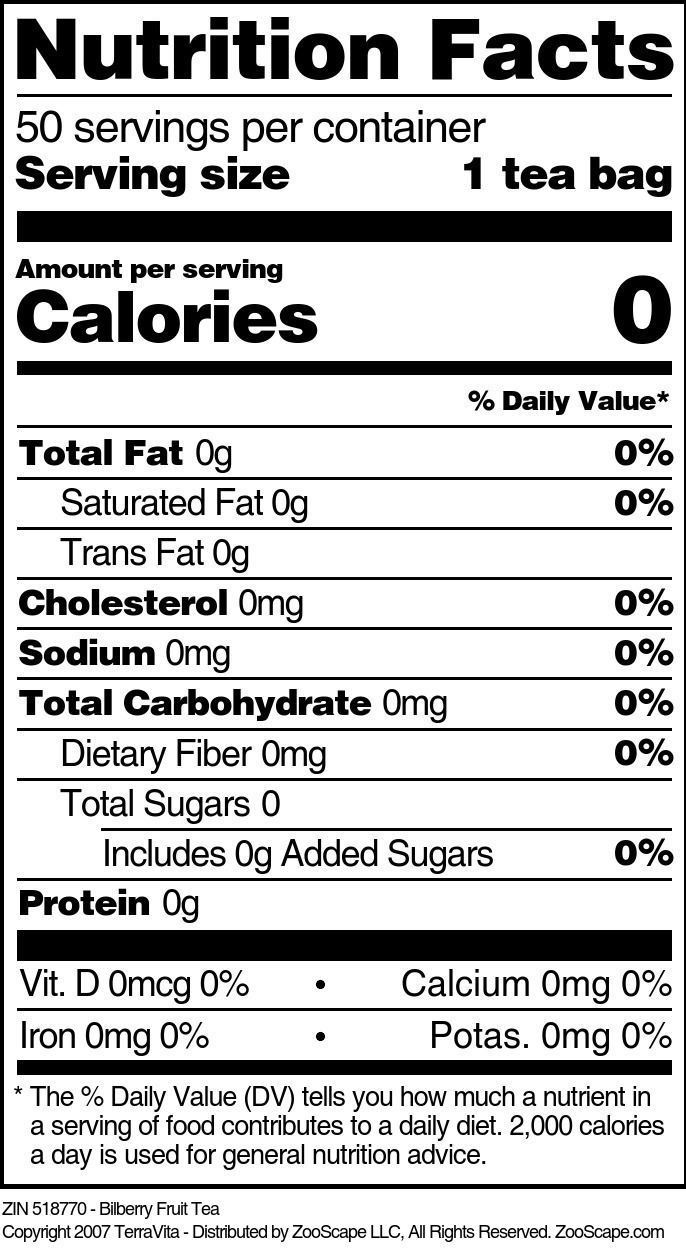
Bilberry Fruit
| Images | Product Name | Size | ZIN | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart |
| Bilberry Fruit - 450 mg | 100 capsules | 518764 | $27.57 | |||
| Bilberry Fruit Powder | 4 oz | 518765 | $28.69 | |||
| 1 oz | 518766 | $12.51 | ||||
| Bilberry Fruit Cream | 2 oz | 523877 | $38.67 | |||
| Bilberry Fruit Salve | 2 oz | 523878 | $42.43 | |||
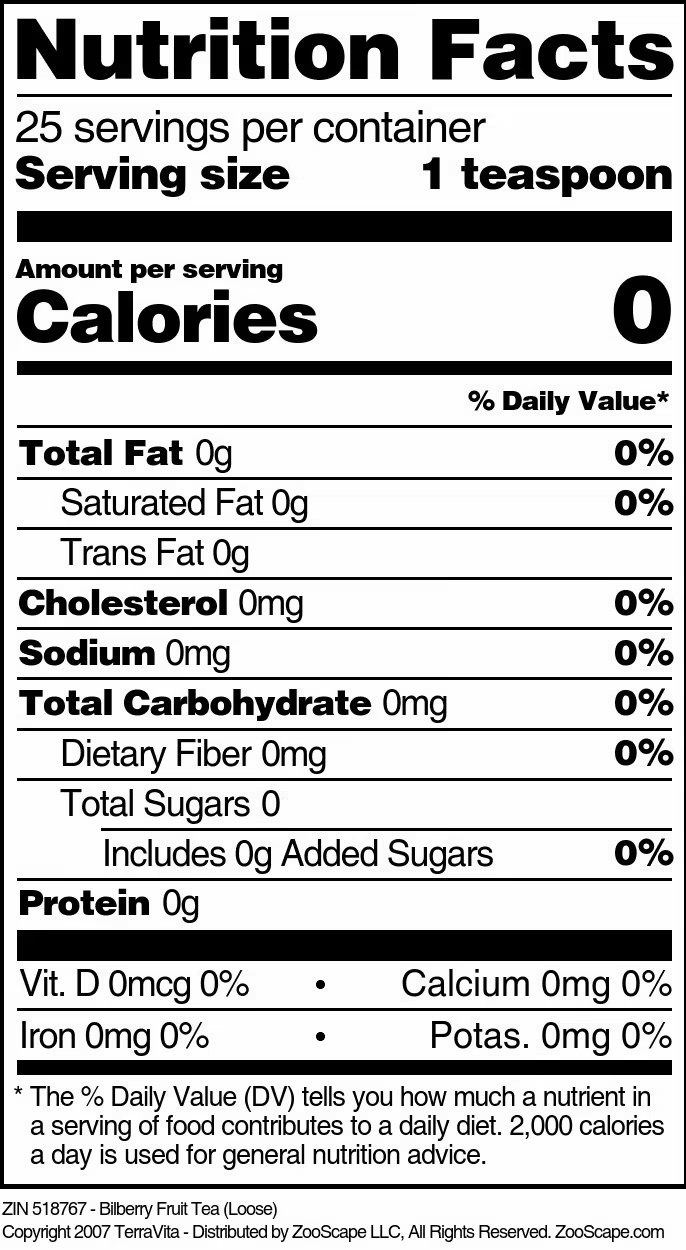
| Bilberry Fruit Tea (Loose) | 4 oz | 518767 | $46.55 | |||
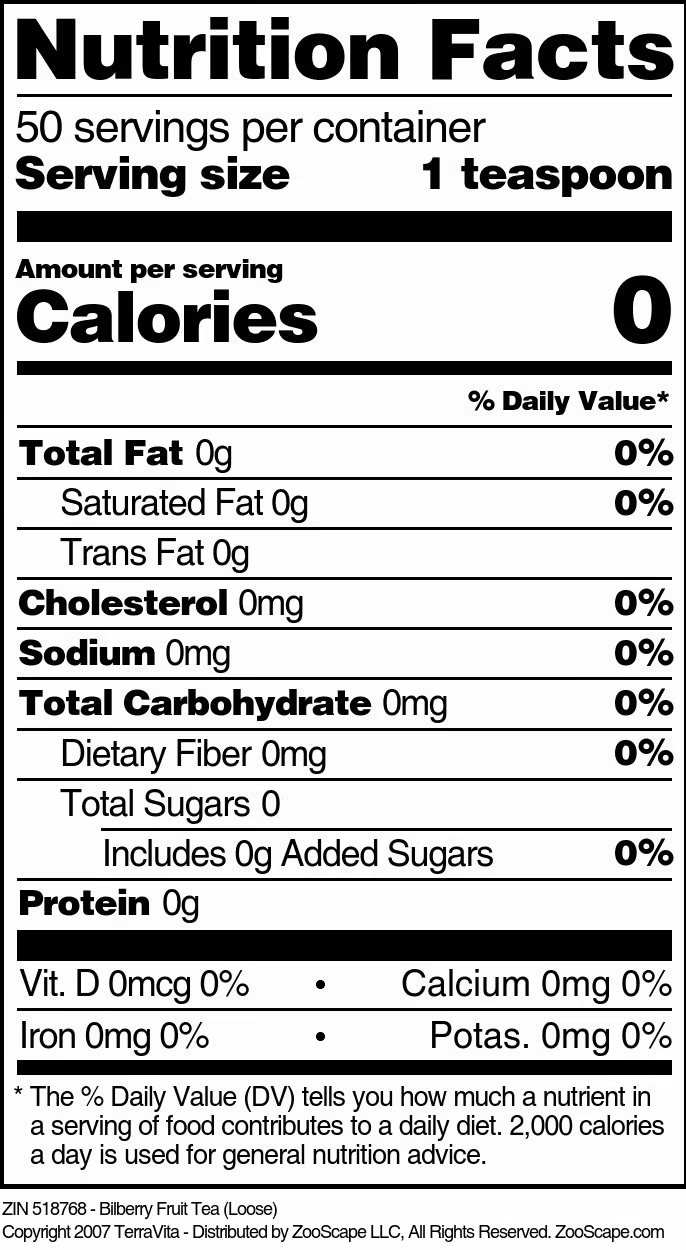
| 8 oz | 518768 | $81.37 | ||||
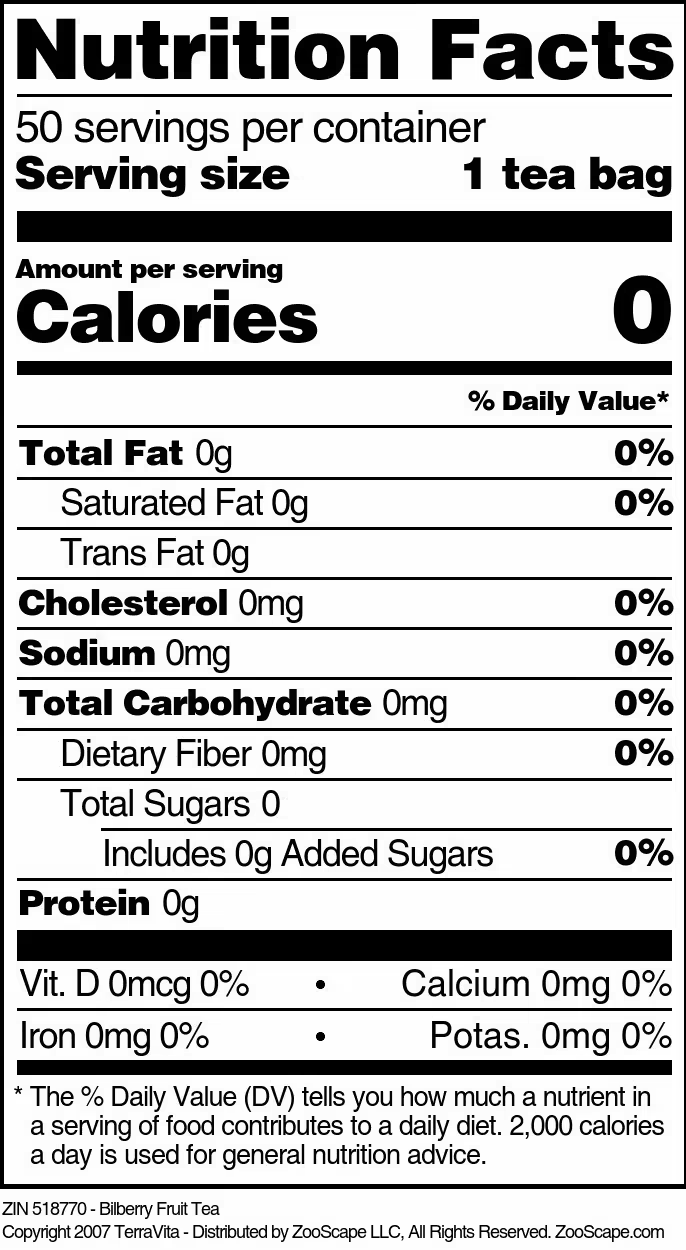
| Bilberry Fruit Tea | 25 tea bags | 518769 | $38.86 | |||
| 50 tea bags | 518770 | $64.65 | ||||
| Bilberry Fruit Glycerite Liquid Extract (1:5) | 1 oz - No Flavor | 522112 | $64.71 | |||
| 1 oz - Strawberry | 522113 | $71.54 | ||||
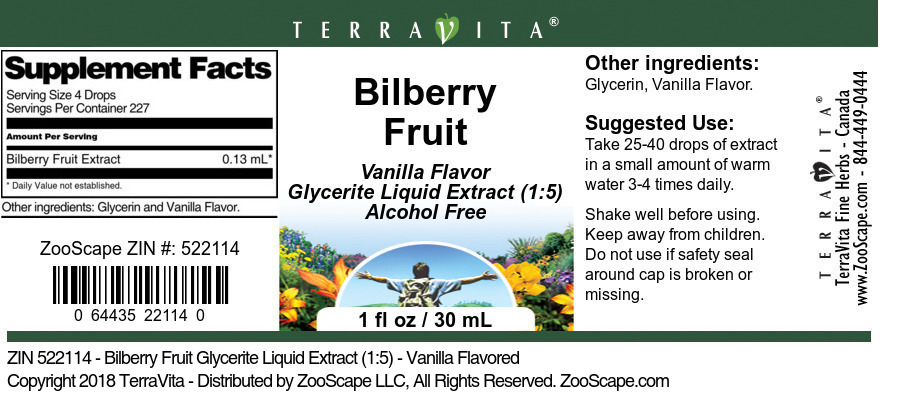
| 1 oz - Vanilla | 522114 | $71.54 | ||||
| 1 oz - Chocolate | 522115 | $71.54 | ||||
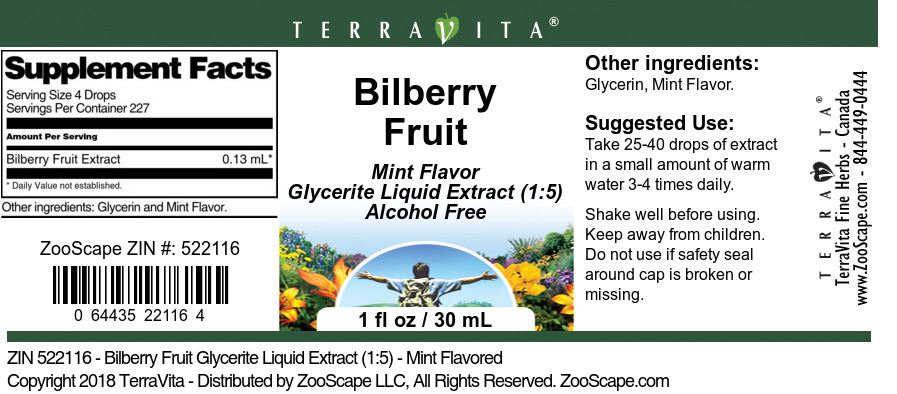
| 1 oz - Mint | 522116 | $71.54 |
Bilberries attracted heightened interest when World War II British Royal Air Force pilots reported improved visual acuity on night-time raids after consuming them. Subsequent studies confirmed their effectiveness in improving nighttime vision, faster restoration of vision after a glare, and in the support for many other eye disorders, including diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, vision, and of varicose veins.
The dried berries have a long traditional use in the support for diarrhea and dysentery. The leaves of this berry, and of the closely related huckleberry, are very effective as a tea for regulating blood sugar in supporting mild blood sugar level concerns.
Vaccinium myrtillus L.
Synonym: V. oreophilum Rydb.
The genus name (Vaccinium) is of disputed origin; it may have arisen from the Latin vacca, cow, allegedly because cows like eating the plant, or from bacca, berry, in allusion to the numerous berries. The specific term (myrtillus) is a reference to the myrtle-like leaves.
Vaccinium myrtillus should not be confused with V. myrtilloides Michx., the velvet-leaf or sour-top blueberry, which is Canada's most widespread wild species of blueberry, occurring from coast to coast.
English Common Names
Bilberry, dwarf bilberry, blaeberry (a Scottish name meaning blue berry), mountain bilberry, whinberry, whortleberry, whortles, myrtle whortleberry, tradeberry, huckleberry.
Most of these common names have also been applied to other species of Vaccinium, and so are frequently misinterpreted. However, in the context of health usage, "bilberry" normally refers to V. myrtillus.
French Common Names
Airelle, brimbelle, myrtille, myrtille commune, myrtillier commun.
The above names are used in European French. The species is absent from Quebec, and an established French-Canadian name is unavailable, although the name "airelle" is generally used when bilberry extract is sold in stores in Canada. The French-Canadian botanist Bernard Boivin provided the name "myrtille" in his Flora of the Prairie Provinces.
Morphology
Bilberry is a small (5-30, rarely 60 cm tall), somewhat spreading, perennial, deciduous, shrub with slender angular branches arising from a creeping rhizome. Plants are usually shorter at higher elevations. The roots are slim (1.5-2 mm in diameter), much-branched, and often form an interconnected mat in the top 5 cm of substrate. The leaves are 10-30 mm long and bright green. The flowers are globular and waxy, with pale-green or pinkish petals 5-6 mm long. The bluish-black (occasionally reddish, bluish, or blackish), globose, flat-topped berries are 5-10 mm in diameter, sometimes covered when ripe with a delicate grey bloom; they have a slightly acid, sweet flavor. The berries may contain up to 40 seeds, although generally only half this number are viable.
Classification and Geography
Vaccinium myrtillus is classified in Vaccinium section Myrtillus, characterized by a 5-celled berry and stamens enclosed within the petals when the pollen is released. In Europe, hybrids (known as V. x intermedium Ruthe) with V. vitis-idaea L. have been reported. Bilberry has at least seven North relatives in section Myrtillus centered in the Pacific Northwest. Of these, the mountain bilberry (V. membranaceum Douglas ex Hooker) has the largest fruit, ranging to 20 mm in diameter, and thus could be employed to increase yield. The Cascade bilberry (V. deliciosum Piper) is of potential interest in breeding and crop development because of its excellent fruit flavor, cold-hardiness and blossom frost resistance.
Bilberry is found in most of Europe, but only on mountains in the south. There are some populations in southwestern Greenland that are thought to be ancient European introductions. The species also occurs in Asia. In North America it is found in two areas of the Rocky Mountains (one in southeastern British Columbia and southwestern Alberta through Washington to central Oregon, the other in central Colorado, adjacent Utah, north-central New Mexico, and southern Arizona).
Ecology
Bilberry occurs in various climates in damp woodlands, heaths, and moors. It prefers filtered shade and moist, acidic, fertile soil. In North America it is found in open, moist coniferous woods, hillsides, hummocky seepage slopes, and moraines above 1600 m. The plants are cold-tolerant at least to -20°C, and much lower when protected by snow cover. Clear-cutting of the trees may be harmful to the plants as a result of mechanical injury, and increased frost and drought injury. Although bilberry is relatively fire-tolerant and resprouts after fires, it is most frequent where burn intervals are relatively long (up to 100 years). Fire suppression may lead to dense conifer forests providing insufficient light for berry production. Similarly, areas replanted with conifers may not supply sufficient light for good growth.
Pollination is by bees. The berries are eaten by many birds and mammals, including bears, and the foliage and twigs are browsed by some mammals. As with many other species of Vaccinium, birds and mammals are known to disperse the seeds. Reproduction is both by seeds and by vegetative spread.
Medicinal Uses
The bilberry has been used in folk tradition for centuries, perhaps even for millennia (although it is difficult to establish the precise identity of some Vaccinium species used in past times). Bilberry extracts are popular and are commonly marketed in Europe, and by numerous North supermarkets, drug stores and rejuvenateth stores. Diverse medicinal claims are made for extracts of bilberry; the chief applications are noted below. Numerous scientific studies (more than 70) have been conducted that provide at least some support to the various claims.
Strengthening of Cardiovascular System
Bilberry is believed to strengthen capillaries, allowing them to stretch without breaking or leaking, so that red blood cells can squeeze through tighter vessels, thereby benefitting blood flow. This can be used to help support bruising, and also varicose veins and "spider" veins which result from leakage of blood from capillaries. In past times in Europe, the herb was used prior to surgery to lessen bleeding, and even today some European doctors prescribe bilberry extracts before operations to reduce post-operative bleeding. Claims have been made that bilberry may support healthy blood pressure levels.
Vision
Bilberry has been shown to improve vision, especially night vision. During World War II, pilots and navigators of the English Royal Air Force consumed large quantities of bilberry preserves, particularly before night missions, in the belief that this improved vision. The proposed explanation is improved blood flow to the capillary-rich retina of the eye. The resulting improved eye function has been said to reduce eye fatigue and support healthy vision and common myopia (near-sightedness).
Blood Sugar Levels
The berries and especially the leaves of bilberry have been used in folk-medicine support for blood sugar level concerns. Bilberry leaf has a reputation as a "blood sugar-reducing" drug, useful in "antidiabetic" (against high blood sugar levels) teas. Although it is not widely used to help support good blood sugar levels today (insulin therapy has become standard approach), it is interesting that very high levels of chromium are found in bilberry leaves, and that there has been suspicion that chromium may have a role to play in the support for blood sugar level concerns. Also, myrtillin (methoxylated glucoside of gallic acid) in bilberry leaf can be used to help support hyperglycemia and normalize blood sugar level. An allied question that has not yet been sufficiently clarified is whether or not the improvements in blood circulation associated with the use of bilberry (discussed above) are useful for the potential to help support symptoms of circulatory disorders associated with blood sugar level concerns. As noted below, because of toxicity the consumption of bilberry leaf is generally discouraged today. hisuliii therapy can debilitate some people, and herbal products capable of safely reducing the need for insulin could be advantageous.
Digestive Disorders and Mucous Membrane Inflammation
Bilberry (both leaf and berry) tea has been used against diarrhea and as a support for nausea and indigestion. Bilberry has considerable taninn content, and the astringent action of the tannins is believed to be responsible for its effectiveness in supporting digestive disorders, and for topical (surface) support for mild inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat. Numerous herbs with tannins are also known to have the same useful properties, and bilbeny is not especially useful for these purposes, although some herbal preparations with bilbeny are available in Europe specifically for digestive disorders. As noted below, the leaf is toxic and prolonged consumption is hazardous. Fresh berries seem less effective than dried, older berries for helping support digestive disorders, perhaps because the tannins are not in a suitable chemical form until after drying has taken place.
Urinary Tract Health
Bilberry has at least some of the beneficial properties of cranberry for maintaining urinary tract function and relieving infections (see chapter on cranberry for details).
Antioxidant
Flavonoids such as found in bilberry fruits are natural antioxidants, which are medicinally effective because they disarm damaging free radicals. Free radicals are highly reactive chemical fragments produced during metabolism in the body, that can impair cell function.
Chemistry
Anthocyanidin flavonoids responsible for the deep bluish color (often in the form of colorless precursors, proanthocyanidins, in the fresh plant) are believed to be the key medicinal compounds of bilberry. The most significant bioflavonoid in bilberry appears to be myrtocyan. Dried berries of bilberry contain about 0.7% anthocyanins. The dried berries of several other wild species of Vaccinium have been shown to have much higher content of anthocyanins, so that it is possible that future research may show that these other species are even more desirable as useful plants than bilberry. Other medicinally significant constituents (tannins, myrtillin, chromium) are discussed above.
Non-medicinal Uses
The berries were extensively eaten by Natives, including the Kootenay, Carrier, and Shuswap tribes. As with other Vaccinium species, bilberry fruit has long been popular in both Europe and North America for jams, jeffies, preserves, pie fillings, and wines. Bilberry is of value as a nurse crop for Douglas fir seedlings. This attractive, hardy, shade-tolerant, low-growing shrub makes an interesting edible landscape, which is very ornamental in the autumn when the leaves turn red. Root cuttings can be transplanted to disturbed sites to reduce erosion, at the same time providing a natural food and cover for wildlife. In some parts of the Rocky Mountains problems with black and grizzly bears could be reduced through effective management of natural stands of bilberry. A larger supply of the berries would reduce bear foraging in populated areas and campsites.
Agricultural and Commercial Aspects
Bilberry is harvested mostly from native stands in North America and Europe and has consequently received much less attention from plant breeders than the cultivated species of Vaccinium, including the cranberries and blueberries. Most cultivated blueberries are stimulated to produce many young flowering and fruit ing branches by heavy pruning of the shrubs. However, this practice is unsuitable for bilberry, which produces most of its fruit at the base of older branches.
Bilberry has a well-deserved reputation as a useful herbal health and therefore promises a growing market. North wild bilberry is not readily accessible (the plant grows in mountainous areas) and so cultivation is desirable. Although not extensively cultivated in North America, natural stands are known to produce up to 100 kg (fresh weight) of berries/ha; a much higher production is likely possible under cultivation. There is considerable information in the European (foreign language) literature on cultivation and management techniques. While there is a large available supply from Europe, the development of a North supply is a worthwhile enterprise.
Myths, Legends, Tales, Folklore, and Interesting Facts
- The name bilberry is derived from the Danish bollebar, meaning dark berry. However, not all berries are dark, and a white-fruited ornamental form is known. North Indians preserved berries of Vaccinium species in various ways. In the North, berries were placed in seal oil, or stored in leather bags deposited in the permafrost. Indians commonly dried berries in the sunshine or by a fire.
- During the latter part of the First World War, England experienced a shortage of aniline dye, formerly imported from Germany, and the pigments from blue-black berries were substituted. So much of the bilberry crop was purchased by dye manufacturers that there was little available for making jam.
Vaccinium myrtillus L., commonly called bilberry, huckleberry, whortleberry, and blackberry. The French for bilberry is Myrtille; in German, Hiedelbeere. Bilberry is a very close relative to cranberry and contains many of the same ingredients.
Source
V. myrtillus, known as bilberry, can be found in most European countries, but it is a hardier plant than its cousins, growing equally well in forests and moorlands. All contain flavonoids, phenolic acids, tannins, and glycosides in various proportions, depending on the variety, and from which part of the plant it is obtained.
Traditional Support Uses
Bilberry fruits have traditionally been used to help support acute cases of diarrhea. Extracts of the leaves have been used to help support good blood sugar levels, urinary tract health concerns, and as "metabolic stimulants."
Commission E Recommendations
Bilberry can be used to help support diarrhea, oral or pharyngeal inflammation, and sore throat. Because of reports of jaundice associated with chronic use, the Commission placed the leaves on its unapproved list.
Possible Effects
Bilberry contains relatively high concentrations of flavonoids (quercetin and myrecetiri) and anthocyanidins. In the test tube, these chemicals fight the oxidation of low density cholesterol (LDL), and LDL oxidation leads to coronary artery problems. These same flavonols and anthocyanidins are found in red wines and grape juice. Many researchers believe their presence helps explain why the French, who drink much more red wine, and eat much more fat than s, have fewer heart attacks. In Germany, products made with bilberry fruit (but not the leaves), can be used to help support diarrhea. Products made with bilberry leaf, however, are not approved for sale, because long-term use is associated with jaundice and weight loss
Dosage
For the support for diarrhea, Commission E recommends 20 to 60 grams per day of the fruit.
TerraVita exists to meet and ensure your family's health and wellness without the harmful effects or chemicals and prescription medications. We strive to make all of our products affordable and reliable and are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you and the ones you love. TerraVita has become a trusted household name for many families and can bring you and yours the very best herbal supplements, blends, teas and spices that are on the market today.
TerraVita is packed in tamper-proof, food-grade, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of TerraVita teas, herbs and supplements in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
Bianca Rosa is an exclusive line of premium-quality natural products sourced from only the finest and purest ingredients from around the world. Bianca Rosa is hallmarked by the highest possible standards of purity, stability and freshness. All Bianca Rosa products are prepared with the highest level of quality control, from the raw materials used through the entire manufacturing process, up to and including the moment that the finished product is sealed for freshness and shipped to you. Our highest possible standards backed by our personal guarantee.
Bianca Rosa makes all products as affordable as possible and we are constantly searching the market to maintain our affordability and to look for new ways to serve you. Bianca Rosa has been a trusted household name for many families throughout the world since the 1990s. Bianca Rosa is packed in tamper-proof, recyclable containers.
ZooScape is proud to be the exclusive distributor of all Bianca Rosa products, including creams, salves and oils in the United States, Canada and around the world. Please direct all wholesale and bulk inquiries to 1-844-449-0444.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Products are intended to support general well being and are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent, or cure any condition or disease.